Mixed-mode chromatography: a versatile tool for the purification of recombinant proteins
The purification of recombinant proteins has its unique challenges such as cumbersome operation, impurities hard to remove and low recovery. Say Hi to mixed-mode chromatography, a secret weapon in bio-processing to solve your problems with ease.
Mixed-mode chromatography, also known as multi-modal chromatography, is a method combining multiple interactions including ion exchange chromatography(IEX), hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) and hydrogen bond interactions. Traditional chromatography method only relies on single interaction (e.g. interactions between charges of IEX resins, hydrophobicity of HIC resins). In comparison, mixed-mode resins can deal with complex samples more flexibly as a result of multiple interactions provided by their ligands.
After the expression of recombiant proteins, host cells will produce many impurities. For example, host cell proteins (HCP), nucleic acids, endotoxins and protein aggregates formed by protein itself. In traditional purification process, several steps are needed, leading to complication in processing optimization and low recovery. By contrast, mixed-mode chromatography enjoys advantages such as combined interactions, reduced processing steps and increased recovery.
The followings are advantages of mixed-mode resins in the purification of recombinant proteins.
Advantage 1: High selectivity
For impurities in extremely similar structure(e.g. protein aggregates, degraded antibody fragments , charge isomers), traditional method are usually failed to perform efficient purification. Mixed-mode chromatography resins possess multiple interactions. For instance, the benzene ring and carboxyl groups of Diamond MMC resin can precisely identify target proteins and effectively remove the above-mentioned impurities, resulting in higher purity.
Advantage 2: Excellent salt tolerance
Traditionally, It is necessary to dilute or dialysis samples to reduce salinity before purification. However, mixed-mode resin can work effectively under relatively high salinity.
Revolutionary application: Direct capture! Sample can be loaded using clarified cell culture supernatant(usually in high salinity). This eliminates buffer dilution/buffer exchange step, which simplifies process, saves time, reduces cost and sample loss, as well as improves recovery.
Advantage 3: Flexible elution strategies
The elution of target proteins will no longer rely on single method(e.g. by adjusting salinity or pH). It is possible to selectively weaken single or several interactions by adjusting pH, salinity or additives, enabling mild, efficient and highly specific elution while retaining protein activity.
Advantage 4: Simplified purification process
Higher selectivity and binding capacity eliminate unnecessary steps. For example, a well-designed mixed-mode purification process can achieve performance traditionally requires IEX+HIC method. This helps to reduce processing time, improve recovery and cut production cost.
Bestchrom provides multiple mixed-mode resins for the choice of customers in bio-processing sectors. Reins available are MMC mixed-mode resins, MIX-A mixed-mode resins and Layer mixed-mode resins. Moreover, pre-packed columns are also available for the convenient usage in all stages from R&D, pilot scale to production scale.
Case study
A recombinant pichia pastoris fermentation broth was purified by Diamond MMC.
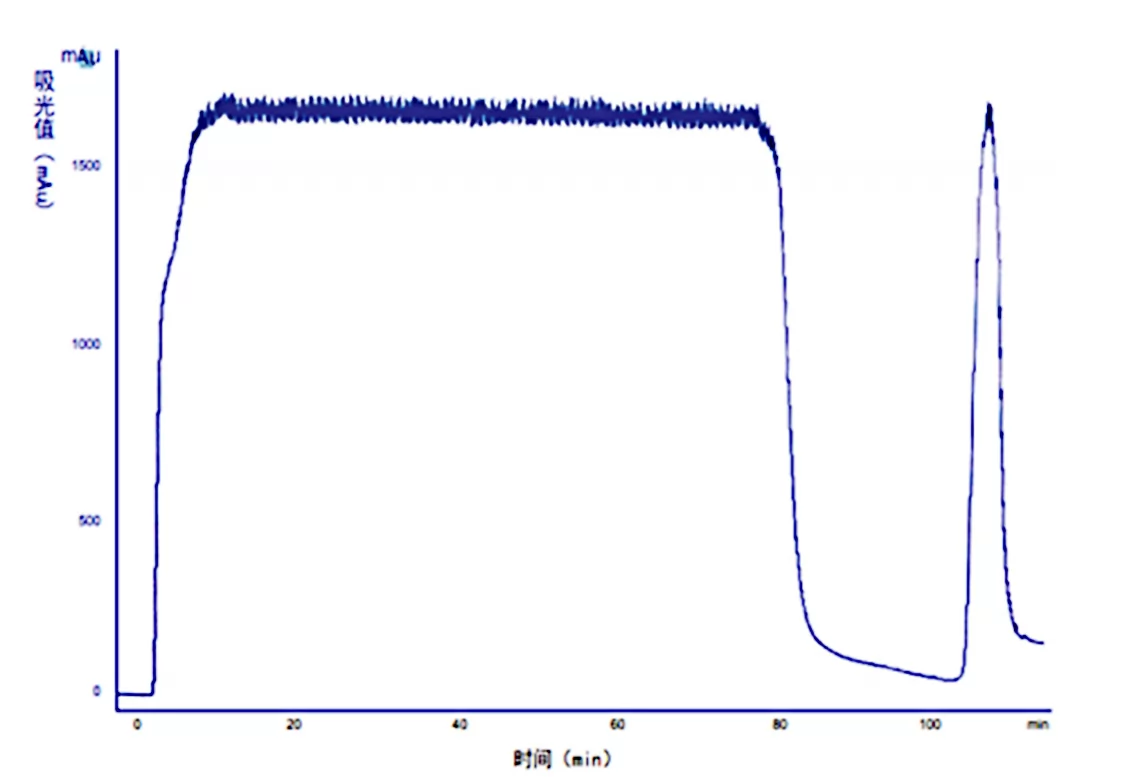
Fig.1 Diamond MMC Chromatogram
Column:Ezload 50/20 Diamond MMC
Equilibrium buffer:20mM PB,0.4M NaCl,pH6.5
Elution buffer:20mM PB,1.5M NaCl,pH6.5
Sample:300mL of a recombinant pichia pastoris Fermentation broth
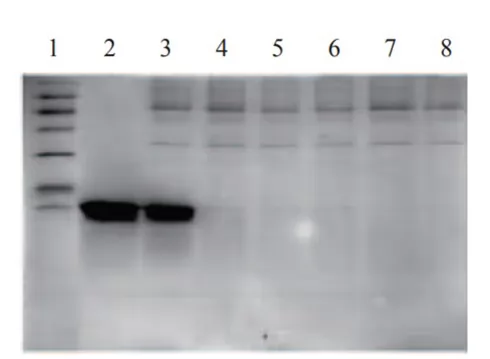
Fig.2 Electrophoretogram
Lane 1: Marker Lane 2: Elution
Lane 3: Fermentation liquid Lane 4-8: Flow through
Tips for use:
As the use number of resin increases, contaminants accumulate on the chromatography column. Cleaning-in-place can prevent the accumulation of contaminants and keep the column at a stable working state. Determine the frequency of CIP according to the degree of contamination (if the contamination is serious, CIP should be carried out after each use to ensure reproducibility of the results).
The recommended CIP for different types of impurities and contaminants:
• Tightly-bound proteins: wash with 2~3CV of 2M NaCl
• Strong hydrophobic proteins and precipitating proteins: wash with 1M NaOH of 2~3CV first, then wash immediately with 5~10CV of pure water.
• Lipoproteins and lipids: wash with 5~10CV of 70% ethanol or 30% isopropanol first, then wash with 5~10CV of pure water.








.png)