Fundamental principles of chromatography purification
Chromatography, as an important means to achieve high purity separation in the research and production of biopharmaceuticals, is widely used in the purification of various macromolecules including vaccines, antibodies and recombinant proteins. Chromatography resin is the key to efficient purification process despite of being seemingly insignificant beads.
The purpose of this article is to introduce four chromatography methods in terms of separation principle, advantages, applicable scenarios and tips for resin selection, so as to promote your process development and technical understanding.
01 Size exclusion chromatography: do separation by sizes
Principle
size exclusion chromatography is based on the sizes and shapes of different biomolecules. Because of the porous structure of SEC resin, smaller molecules will be travel longer path and therefore have later peaks. The key to choose SEC resin is the right fractionation range while still considering mechanical property and scalability of resin.
Size exclusion chromatography terms:
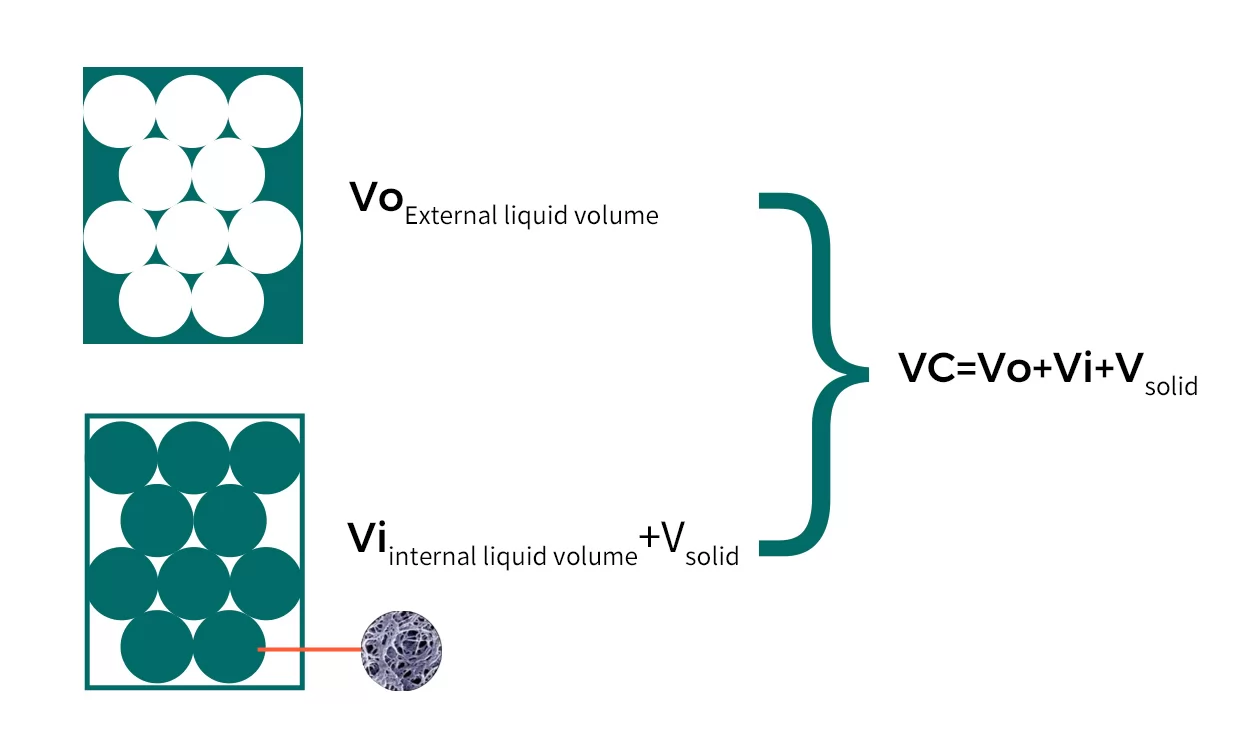
Fig.1 Size exclusion chromatography terms
Size exclusion chromatography process
macromolecules are the first to leave column, followed by medium molecules, micromolecules are the last to leave column. The whole process will take a CV of buffer to go through the SEC column.
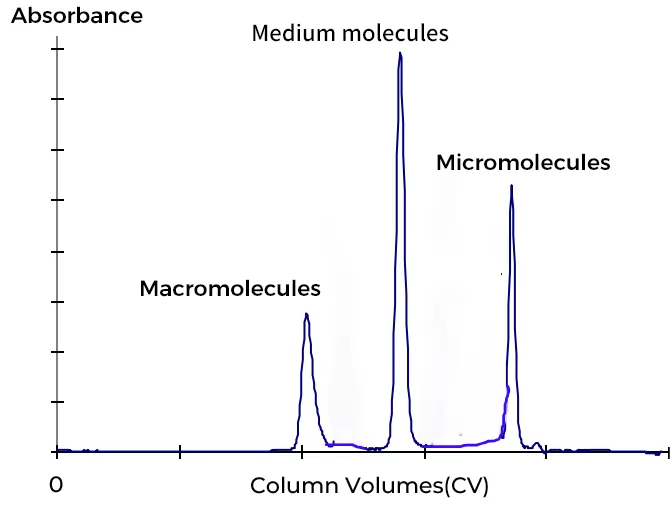
Fig.2 Chromatogram of SEC resin
Commonly used buffer:
Buffers: Tris-HCl(pH 7-8), phosphate buffer(pH 6-7.5), low concentration NaCl (eg. 150mM to reduce adsorption)
Characteristics of different base matrixes
Bestdex: cross-linked dextran, for the rapid separation of components with wide disparity in molecular weights. For example, desalting, buffer exchange
Bestarose: Cross-linked agarose, provides excellent resolution and flow rate under intermediate pressure. Suitable for the polishing of production scale macromolecules.
Chromdex: Highly cross-linked agarose and dextran, high resolution, high rigidity, ideal option for polishing stage in chromatography process.
Tips for resin selection:
Pore size of every resin will fall into a certain range. The key to choose SEC resin is the right fractionation range while still considering mechanical property and scalability of resin.
Typical applications
Fraction isolation(buffer exchange ): remove small molecules from bigger molecule groups. Alternatively, used for the rapid and simple operation of buffer exchange, sample volume shall be lower than 30% CV.
Polishing: remove impurities other chromatographic method failed to remove such as polymers. Sample loading volume: usually 0.5-5% CV
Qualitative analysis: the determination of molecular weights and molecule distribution
02. Ion exchange chromatography : use charges for binding
Principle
IEX resin is chromatography method Ion exchange(IEX) chromatography is a chromatography method achieving separation based on number and property of electric charges on biomolecules. Macro-biomolecules contain acidic and basic functional groups, which can be changed in terms of charge property and quantity by adjustment of buffer pH. Thus, after binding between biomolecules and IEX resins (with opposite charge property of the biomolecules), biomolecules will be eluted in sequence (molecules with weaker binding will be eluted earlier) if ion strength or pH in mobile phase is altered. By this way, effective purification can be achieved.
Titration curve of protein
Every type of protein possesses unique correlation between net charge and pH, which can be displayed by titration curve.
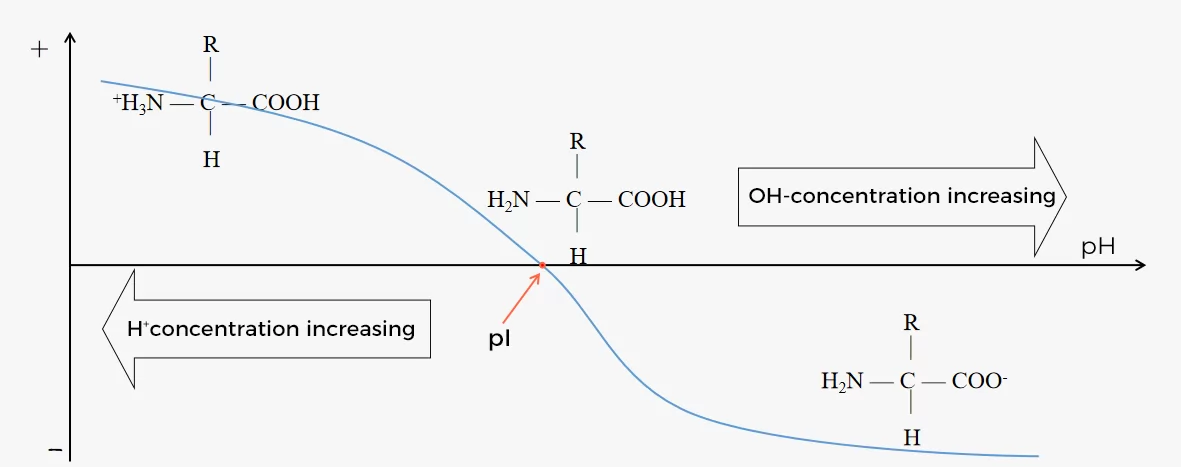
Note: when solution pH is lower than the pI of molecule, molecule will be positively charged(+) on surface; When solution pH is higher than the pI of molecule, molecule will be negatively charged(-) on surface.
Fig.3 Titration curve of protein
Commonly used ligands
|
AIEX resin
|
|
Diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)
Quaternary ammonium ethyl (QAE)
quaternary ammonium (Q)
|
-OCH2CH2N+H(CH2CH3)2
-OCH2CH2N+(C2H5)2CH2CH(OH)CH3
-CH2N+(CH3)3
|
|
CIEX resin
|
|
Carboxymethyl (CM)
Sulfopropyl (SP)
Sulfomethyl (S)
|
-OCH2COO-
-CH2CH2CH2SO3-
-CH2SO3-
|
Table 1. Functional groups of IEX resins
IEX chromatography process
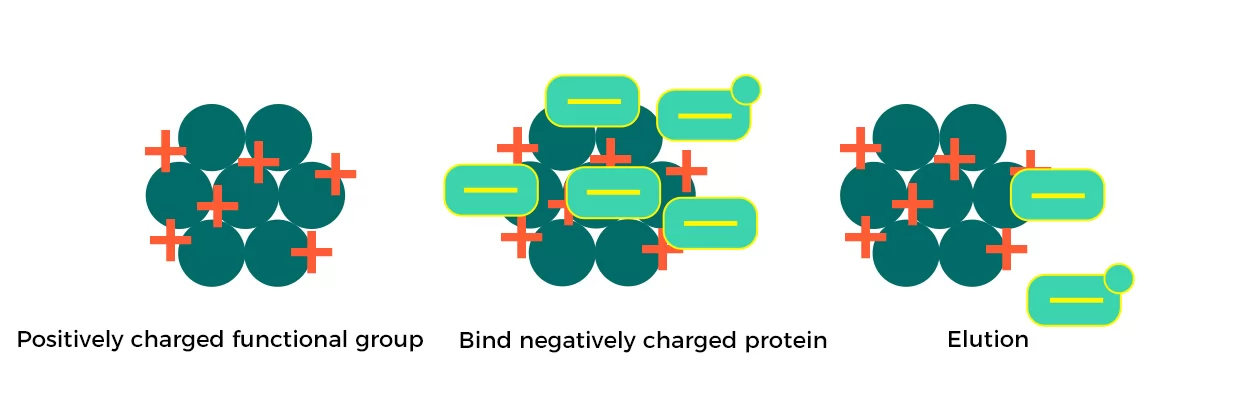
Fig.4 Chromatography process of AIEX resin
Advantages vs disadvantages
Advantages:
• High binding capacity, suitable for production scale-up
• High separation efficiency, wide application (can be used in about 75% of purification process)
Disadvantages:
• Need to optimize pH and salinity
• Need to elution in high salinity condition, not suitable for high salinity condition as a result of unstable sample.
Application
• The removal of impurities (e.g. HCP, DNA) from antibody purification
• Polishing of vaccine antigen
• Capture of recombinant protein and polishing
03. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography(HIC): hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity?
Principle
Based on the hydrophobicity difference on molecule surface ,hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) achieves separation of proteins via reversible interaction between protein and HIC resin. The key of HIC lies in the selection of ligands with appropriate hydrophobicity. That is, proteins with strong hydrophobicity need resins with lower hydrophobicity, and vice versa.
|
Phenyl
|
-O-
|
|
Octyl
|
-O-(CH2)7-CH3
|
|
Butyl
|
-O-(CH2)3-CH3
|
|
Butyl-S
|
-S-(CH2)3-CH3
|
Table 2. Functional groups of HIC resin
Hydrophobic interaction strength of HIC resins
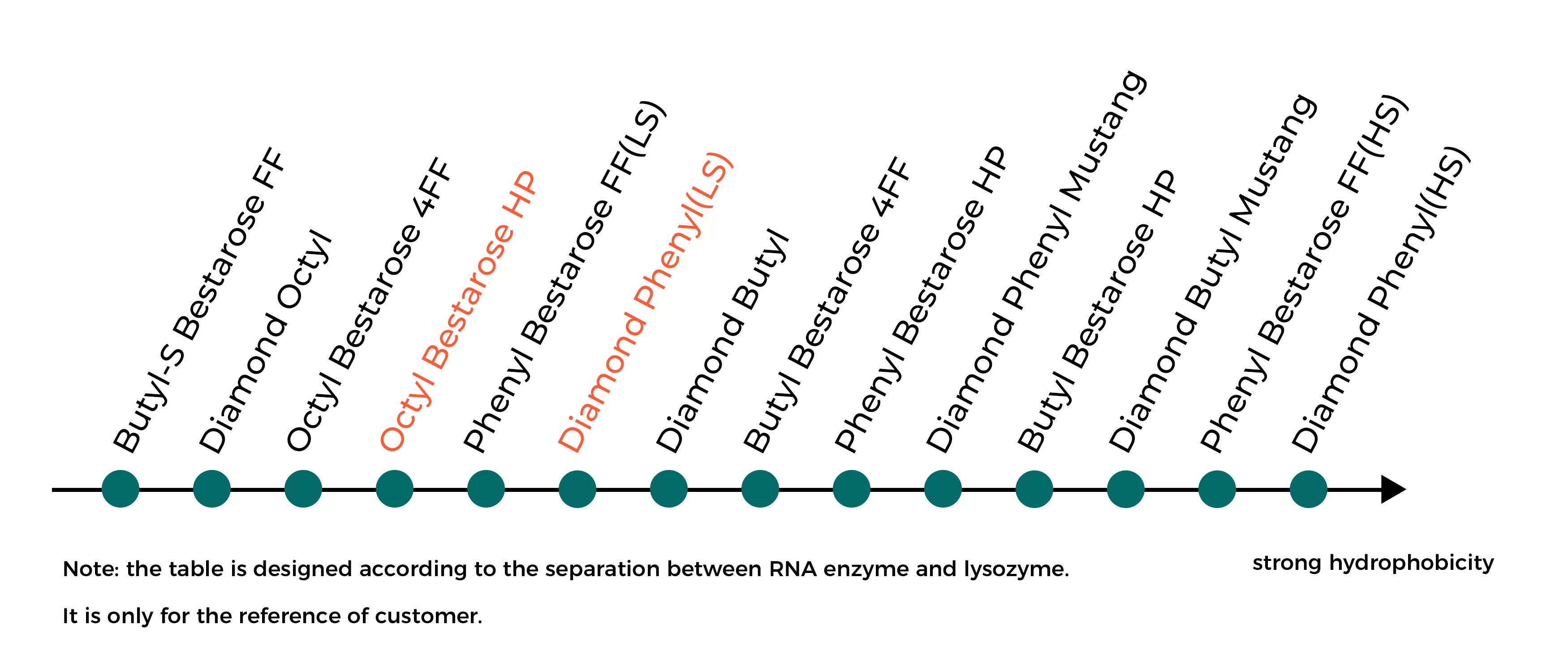
Fig.5 Hydrophobic interaction strength of HIC resins
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography process
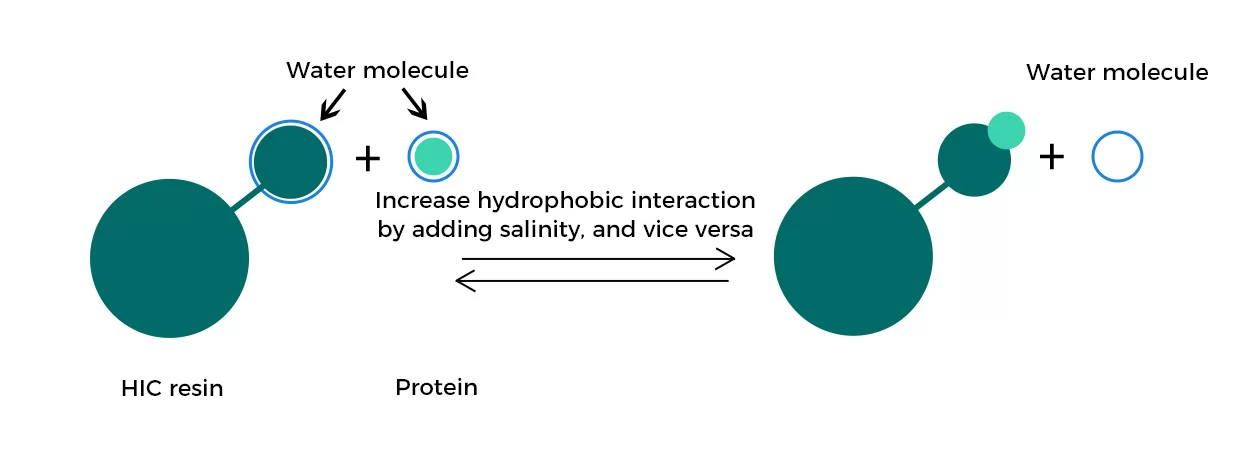
Fig.6 Hydrophobic interaction chromatography process
Advantages vs Disadvantages
Advantages:
• High resolution
• Its feature of “bind in high salinity condition, elute in low salinity condition” means it can be used in combination with other chromatography techniques such as salting out and ion exchange chromatography
Disadvantages:
• High salinity can cause precipitation, it is necessary to keep the salinity at an appropriate level.
• Sensitive to temperature: make sure sample, buffers, columns and chromatography equipment are all at the same temperature before starting chromatography.
• Peak tailing in elution
Typical applications
• Suitable for the capture, intermediate purification and polishing of proteins based on their hydrophobicity disparity.
• The removal of aggregate and fragment of antibody
• The removal of impurities in ADC purification
04. Affinity chromatography: identify the specific adsorption
Principle: Affinity chromatography is a separation method based on the specific interaction among biomolecules. Examples of such can be found in binding of enzyme and substrate, receptors and ligands as well as antibodies and antigens. Since these bindings are both specific and reversible, such method can be used for efficient protein purification. Affinity chromatography enjoys high selectivity, which means it can achieve rapid capture of protein from complex system, as well as 90% or above purity via one-step purification.
|
Enzyme
|
Substrate analog, inhibitor, cofactor
|
|
Antibody
|
Antigen, viruses, cell
|
|
Acetic acid
|
Keywords complementary subtractive sequence, histone, nucleic acid polymerase
|
|
Glutathione
|
Glutathione-S-transferase or GST fusion protein
|
|
Metal ions
|
His-tag protein, natural proteins with histidine
|
Table 3.Common ligands and substrates of affinity resins
Structure of affinity resin
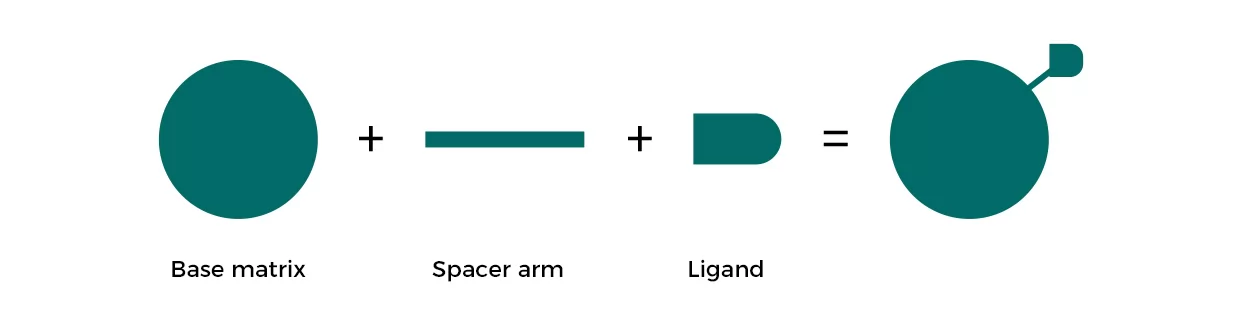
Fig.7 Structure of affinity resins
• Base matrix: porous beads, enables the coupling of ligands, physical and chemical inertness.
• Spacer arm: eliminate space steric hindrance, improve the binding between ligands and target molecules.
• Affinity ligands: reversibly bind to target molecules or molecules of target functional groups
Advantages vs Disadvantages
Advantages:
• High specificity, purity of 90% or above after one-step purification
• Easy operation, used for the initial capture stage.
Disadvantages:
• Relatively high unit price than other resins
• Risk of ligand leakage
Typical applications
• Initial capture of mAb/BsAb
• Purification of tag-proteins
Conclusion
Chromatography technology is the cornerstone of modern bio-pharmaceuticals with resin being the key component. Chromatographic principle is the first step to purification technology. In the future, Bestchrom will cover other topics such as tips for resin selection, process optimization and case studies.








.png)