Lifecycle validation of chromatography resins
Chromatography technology has become an increasingly indispensable step in the processing of biologics. Generally speaking, manufacturing of biologics involves multiple chromatographic steps, where residual impurities are reduced to the lowest level to comply with the safety standards of exogenous materials. Since chromatography resin cost accounts for a significant percentage in the whole manufacturing process, the times resin can be used or the cycles (resin lifecycles) will play an essential role in the cost control of manufacturing process.
Regulatory requirements for lifecycle validation of chromatography resins
On account of the safety and effectiveness of biopharmaceutical drug products, relevant supervision authorities in different countries have specified requirements on the chromatography resin lifecycle and the corresponding acceptance limit.
Table 1. Regulatory requirements for lifecycle validation of chromatography resins
|
Regulatory guidance |
Requirements |
|
Chinese pharmacopoeia 2020 |
General instruction for human use recombinant Mab antibody products |
Process validation shall at least includes acceptable limit for reusability of purification materials(i.e. chromatographic column) |
|
FDA |
Key considerations for the production and testing of human use Mab products |
Pre-set limit shall be given to chromatography resin |
|
EMA |
One CPMP statement |
Most host cells are removed by chromatographic column, whose selection depends on resin quality, preservation condition, cleaning ,sterilization and so on. |
|
GMP 2023 |
Biologics appendix |
The preservation, regeneration and life cycle study of chromatography resin shall be validated |
In addition, PDA publishes Technical report 60-3 Process validation: life cycle method. Attachment 2: production of biopharmaceutical APIs. The report confirms improvement of chromatography resin validation is a key part in process validation.
Factors influencing resin lifecycle decline
During the work life of chromatography reins, the following major factors exert impact on the lifecycle of resins.
(1) The step of purification process and feedstock property(In general, resin will witness a relatively fast drop in lifecycle when capturing crude feedstock, whereas resin will enjoy a relatively slow decline in lifecycle in the polishing step.)
(2) The regeneration, cleaning and preservation procedures of resin.
(3) Column packing and wear-and-tear of column efficiency
Analytical method of resin lifecycle
Analytical method of resin lifecycle shall be able to reflect the scale of commercial manufacturing process, alternatively present the correlation between resin lifecycle and manufacturing scale.
Table 2 Analytical method of resin lifecycle
|
Strategy |
Prospective validation |
|
Method |
Lifecycle studies at commercial scale |
Lifecycle studies at small scale |
|
Test chromatographic column efficiency every N cycles |
Test chromatographic column efficiency every N cycles |
|
Perform a blank run every N+1 cycles |
Perform a blank run every N+1 cycles |
|
Quarantine collected sample in the last N cycles till all detected parameters meet quality standards |
Once getting the resin lifecycle in small scale application, conduct validation at large scale when using suitable security coefficient. |
|
Advantage |
No need of scale-down |
Majority work is done at small scale(faster, more cost-effective), suitable security coefficient, no waste |
|
Disadvantage |
At any time point, risk for N failure is existent. |
Data of scale-down model can merely be regarded as guidance, which shall be confirmed in commercial scale application. |
Note: Supervision frequency (N)can be adjusted according to understanding of process technology and practical situations.
•Scale-down
Prospective study of life cycle validation shall adopt scale-down. Scale-down is based on linear reduction. Specifically reducing column diameter, volumetric flow and sample volume while keeping column bed height, linear flow, sample loading volume(can use worst condition), buffer volume(CV) and elution collection standard unchanged. Meanwhile, other factors including column pressure, sample diffusion, column void and column efficiency shall all be taken into account.
•Carryover
Carryover shall be considered when designing resin life cycle study. Periodic carryover can be used for cleaning procedure efficiency and product residual level. During carryover, conduct chromatographic column process as usual whereas loaded sample is replaced by water or buffer.
Acceptance criteria of resin lifecycle study
Lifecycle of resin shall be defined by the criteria of detection parameters. Criteria of detection parameters can be set as a specific cut-off standard. For example, yield >80%, SEC-HPLC purity >95%, etc. Alternatively, it can also be defined by the consistency among cycles, when no specific criteria will be set.
Table 3. Evaluation parameters of lifecycle study and acceptance criteria (for example)
|
Evaluation parameters |
Acceptance criteria |
|
Evaluation parameters of chromatographic column |
Column efficiency(HETP and As) |
Within the specified standard range |
|
Pressure/flow rate |
No significant change in pressure/flow rate |
|
Resin property |
Parameters including binding capacity and particle size distribution meet specified standards. |
|
Evaluation parameters of chromatography performance |
Chromatogram |
Uniform peaks in chromatogram, no abnormal peak, uniformity among elution peaks. |
Yield(Recovery) |
Within the specified standards |
|
Assessment parameters of product quality |
Product purity |
Within the specified standards, uniformity among cycles |
|
Process-related impurities |
Within the specified standards, uniformity among cycles |
The end-point of resin lifecycle study is usually decided by the number of cycle getting to detection standard, alternatively, cycle number when abnormality among batches can also be used. Generally speaking, conservative method is to multiply the specific cycle number by a security coefficient, so as to define the final chromatographic resin lifecycles.
Case study:Life cycle study of Bestchrom antibody affinity resin Novo-A Diamond
Novo-A Diamond is alkali tolerant Protein A antibody resin based on Bestchrom self-reliant technology. The resin can tolerate CIP with 0.5M-1.0M NaOH, enjoying higher binding capacity and better pressure/flow characteristic.
Sample used in this case was cell culture medium supernatant which contains mAb antibody. In the case, the sample was loaded on Novo-A Diamond resin. After 188 cycles, conduct CIP with 0.1 M NaOH and 0.5M NaOH. Meanwhile, indicators including elution yield, HCP, HCD,Protein A, SEC are detected.
According to final data, Novo-A Diamond enjoys relatively high binding capacity (10% DBC initial value was 67mg/mL). After 156 cycles, 10% DBC value still kept 80% of its initial value. Yield in all cycles and eluted sample purity showed good stability. Meanwhile, HCP, HCD and Protein A residue level were kept at a low level.
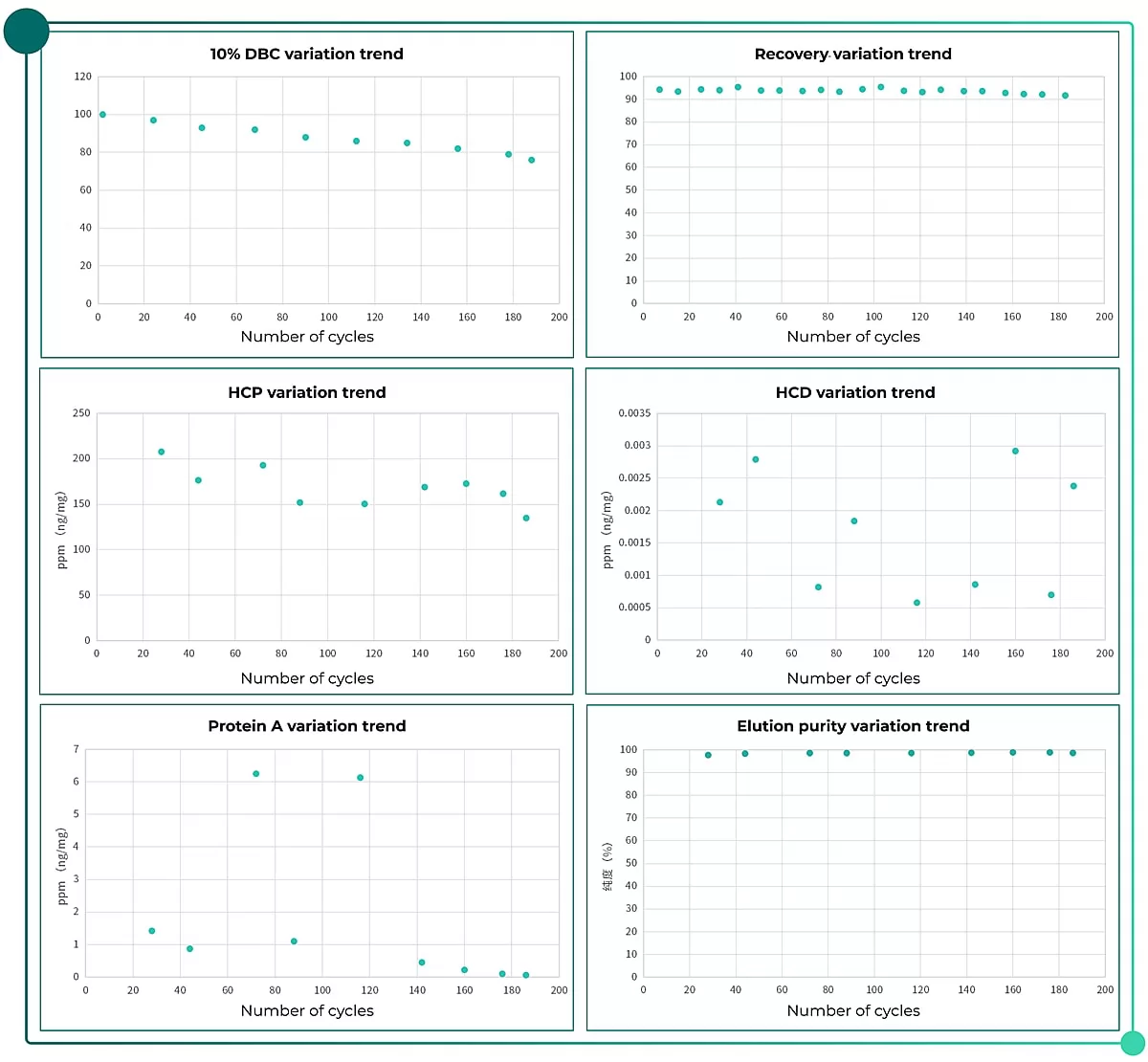
Fig.1 Data comparison of Novo-A Diamond resin life cycle study.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as the vital raw material in the downstream processing of biopharmaceuticals, chromatography resin possesses close relationship between its property and quality of biological drugs. The resin lifecycle validation experiment can not only boost controllability and cost-effectiveness of production process, but also act as a reliable guarantee for commercial scale production.
Reference
[1] General Theory of Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody Products for Human Use, Part III, 2020 Edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia.
[2] FDA “Guidance for Industry:Process Validation: General Principles and Practices”.
[3] FDA “Points to Consider in the Manufacture and Testing ofMonoclonal Antibody Products for Human Use”.
[4] EMA “Guideline on process validation for the manufacture of biotechnology-derived active substances and data to be provided in the regulatory submission”.
[5] EMA “CPMP Position Statement on DNA and Host Cell Proteins (HCP) Impurities, Routine Testing Versus Validation Studies,” CPMP/BWP/382/97.
[6] PDA Technical Report No.60-3: Process validation: A lifecycle approach Annex 2: biopharmaceutical drug substances manufacturing. Parenteral Drug Association: 2021.








.png)