Purification method of collagen
Collagen, as a protein combined with both special structure and function, is widely applicable in biomaterial sectors including pharmaceuticals and aesthetic cosmetics. As the market demand grows rapidly, synthetic technology of recombinant collagen gains gradual maturity and becomes mainstream option in the field. In this article, Bestchrom will share cases of collagen purification based on both natural and recombinant collagens.
Introduction and classification of collagen
Collagen is a structural protein widely found in skin, bone and tendon. Its basic unit is composed of three peptide chains, forming a stable three-strand helix structure. This unique structure enables its vital role in the tissue repairing, tissue engineering and aesthetic cosmetics.
Natural collagen
Natural collagen is extracted from animal tissues(e.g. skins and bones) via physical, chemical and enzymolysis methods.
Acid-base hydrolysis approach: Get animal tissues(e.g. skins and bones) cleaned, sliced and crushed. Dissolve collagen via acidolysis/alkolysis. Get collagen after going through steps including neutralization, filtration, concentration and buffer exchange.
Enzymolysis approach: Get animal tissues(e.g. skins and bones) cleaned, sliced and crushed. Perform enzymatic hydrolysis by specific protease, isolate and get collagen after subsequent steps including centrifugation, filtration and concentration & buffer exchange.
However, to meet higher quality standard, collagen extracted by conventional natural methods is facing challenges such as impurity control (e.g. endotoxin control), presenting stricter requirements on subsequent purification process. BestChrom anion exchange (AEX) chromatography resins are designed for the production of collagen with high purity.
Recombinant collagen
Synthesized by gene engineering technology, recombinant collagen successfully eliminates risks of its animal-derived counterparts such as fluctuation in quality and potential safety concerns. Recombinant collagen production system mainly consists of E.Coli expression system and yeast expression system, which enjoys advantages including high productivity, lower cost and short production timeline. Production process includes steps such as fermentation expression, salting-out, solid-liquid separation, clarification, affinity chromatography and ion exchange chromatography and mixed-mode chromatography.
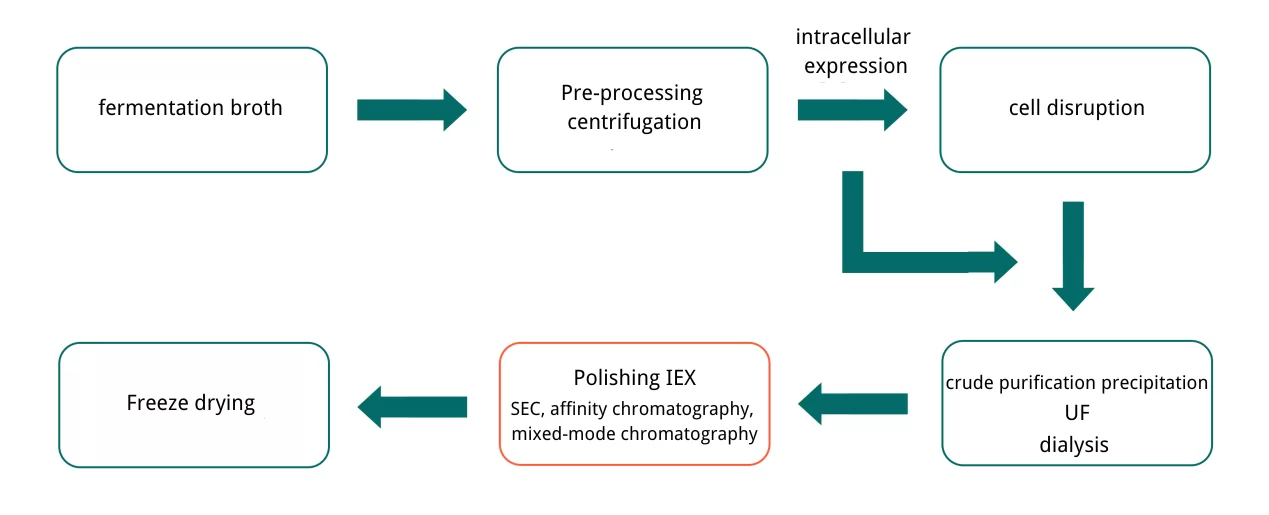
Purification strategy of collagen
The choice of purification strategy for collagen shall be based on expression system and application practice. In case of tag in construction design, it is recommended to choose affinity chromatography for efficient purification. In the absence of tags, it is possible to achieve purification based on disparity between target collagen molecules and protein impurities in terms of charge, hydrophobicity and molecule sizes. IEX, HIC and SEC resins are usually chosen to perform the purification, with mixed-mode resin being an option for subsequent polishing step. It is noticeably that these approaches can be flexibly adjusted to meet different application and purity requirements.
Affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography is an isolation approach based on specific bind and is usually applied in the initial stage of recombinant collagen purification. Specifically, by inserting tags(e.g. His tag) to expressed collagen, target molecules are captured via specific binding. Ni2+ enjoys specific affinity with His tag, which can be captured by IMAC resins such as Ni Bestarose FF or Ni Bestarose HP. Specifically, it can usually get a 80% or above purity via one-step operation due to its excellent impurity removal performance. After that, collagen original solution can be obtained after going through subsequent steps including polishing with SEC resin, concentration and buffer exchange.
Purification process:
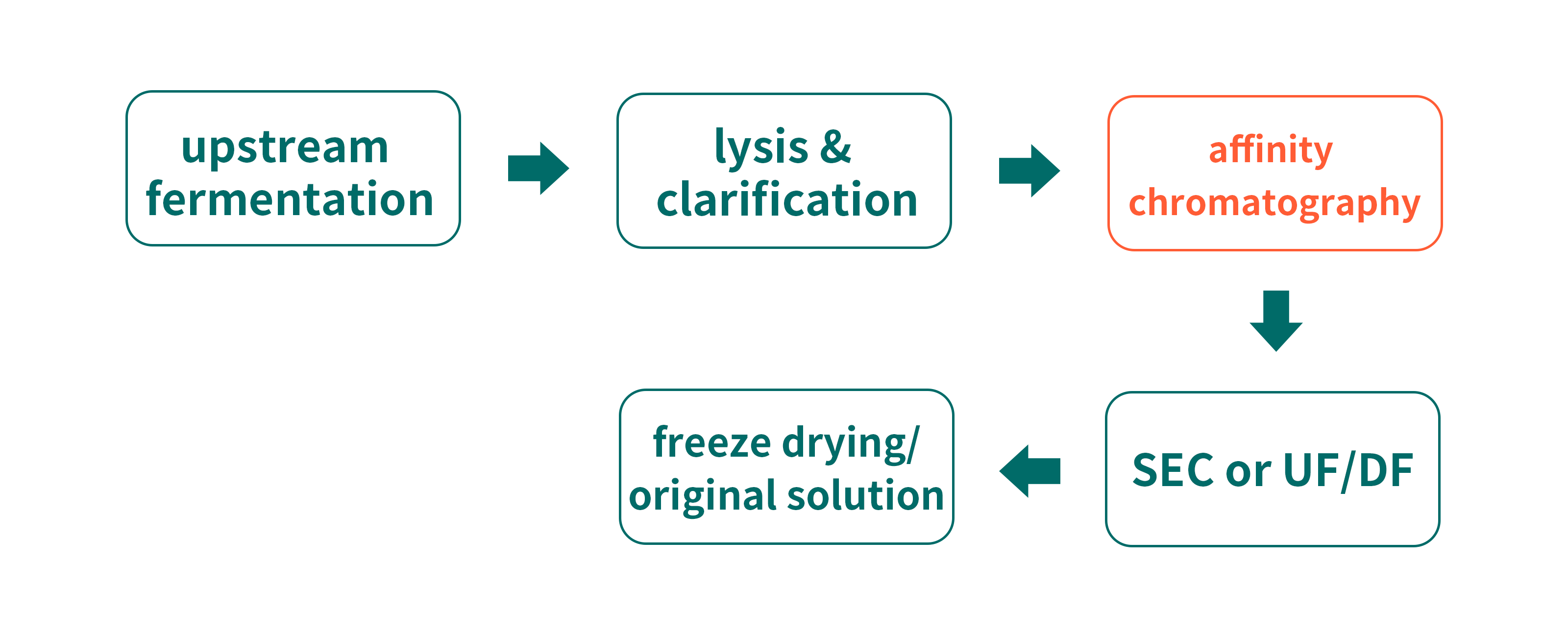
Case study: Ni affinity capture
Ni Bestarose FF being used in the purification of His-tagged recombinant protein.
Column: EzFast 1mL
Bed height: 2.5cm
Buffer A: 20mM PB, 0.5 M NaCl, 20mM imidazole, pH7.6
Buffer B: 20mM PB, 0.5M NaCl, 500mM imidazole, pH7.6
Sample: lysis buffer supernatant of His-tagged recombinant protein expressed by E.coli
Flow rate:0.3mL/min
IEX chromatography
IEX chromatography achieves isolation based on the disparity of charge types and numbers carried by target protein molecules and impurities. Collagen molecules are sensitive to pH and therefore more suitable for acid buffers. AEX chromatography can be applied in the rapid capture of recombinant proteins obtained by intracellular soluble expression of E.coli. AEX resin is the mainstream option in the polishing stage for endotoxin removal.
Purification process:
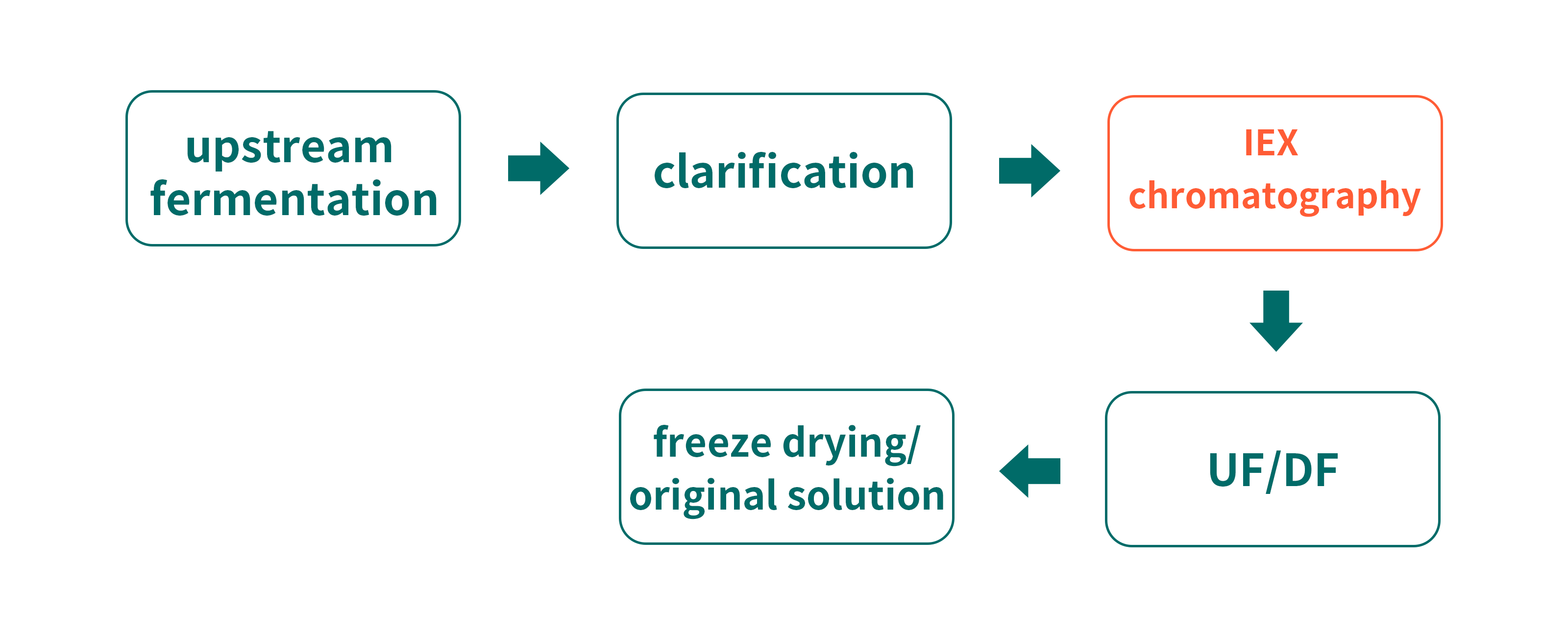
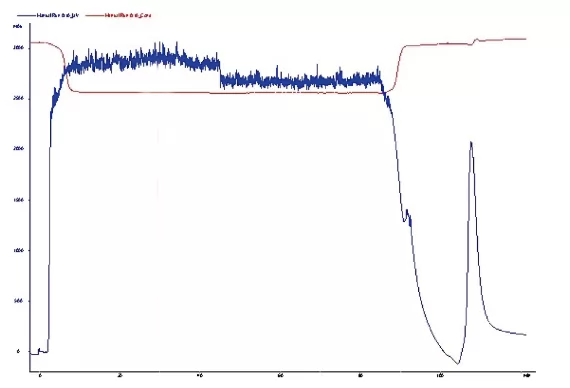
Case study: Diamond CD-S used for purification

In the case, Diamond CD-S resin shows high resolution under linear gradient condition, indicating a successful operation in the isolation of recombinant collagen from impurities.
Mixed-mode chromatography
For some purification projects with special requirements, mixed-mode resins can be employed in case of unsatisfying purification results generated by IEX resins. Mixed-mode chromatography provides wider selection for purification via multiple interactions including charge interaction and hydrophobic interaction. Unlike single-mode purification approach, mixed-mode chromatography enjoys better sample selection by changing pH, conductivity or pH-salt gradient elution.
Purification process:
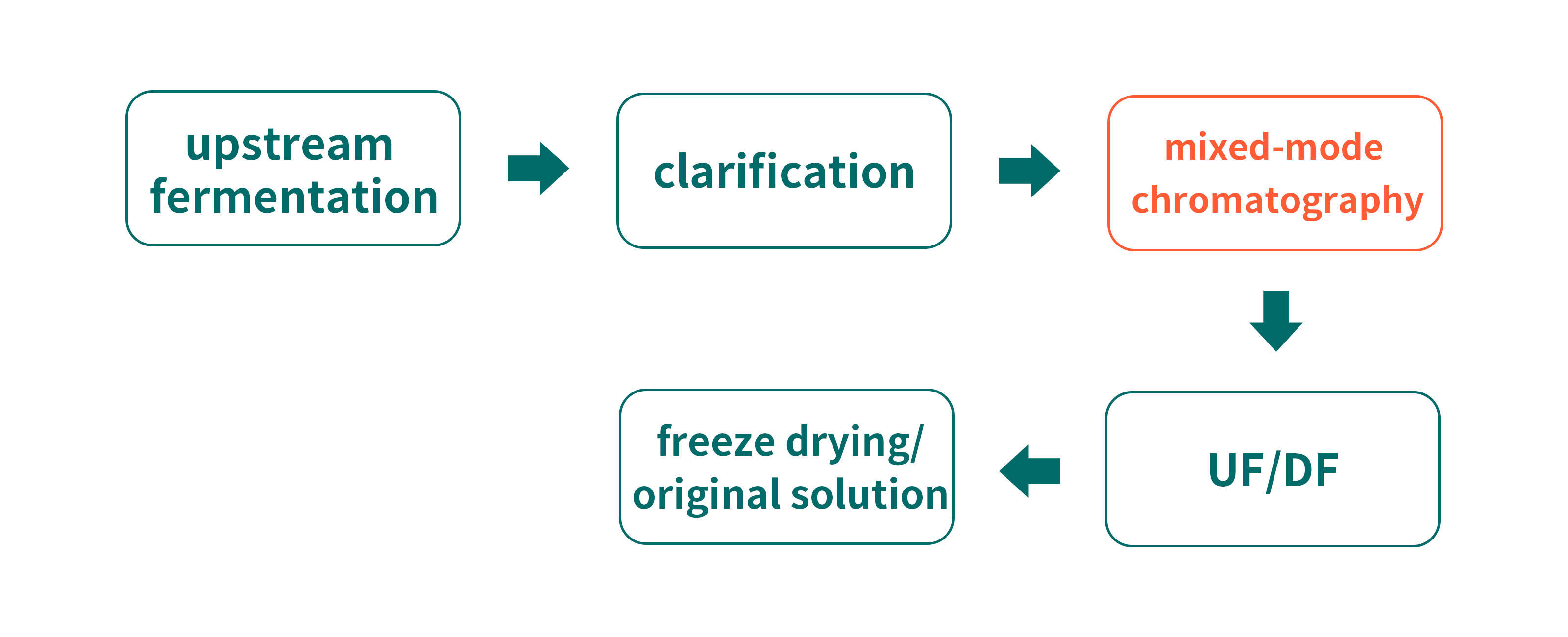
Case study: Diamond MMC Mustang resin used for purification
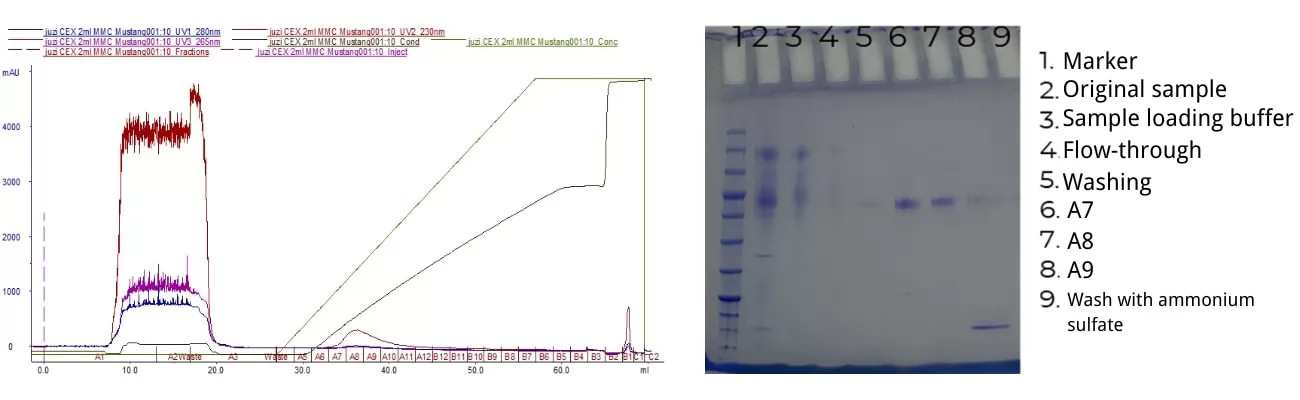
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
Due to high molecular weight, SEC resins are used for buffer exchange. Specifically, using SEC resin to remove affinity tags isolated by affinity resin.
Conclusion
Advanced synthetic technology of collagen provides quality raw materials for fields such as tissue repairing, tissue engineering and aesthetic cosmetics. For both natural collagen and recombinant collagen, suitable purification approach and efficient chromatography resins are key to successful quality control. Bestchrom resins are widely used in collagen purification process from lab projects to processing-scale production due to their excellent performance and lot-to-lot consistency.
Order information for affinity resins:
|
Resin |
Pack size |
Cat.No |
|
Ni Bestarose FF |
25mL |
AA0051 |
|
100mL |
AA0052 |
|
500mL |
AA0053 |
|
1L |
AA0054 |
|
5L |
AA0055 |
|
10L |
AA0056 |
|
IMAC Bestarose FF |
25mL |
AA0061 |
|
100mL |
AA0062 |
|
500mL |
AA007311 |
|
1L |
AA0063 |
|
5L |
AA0064 |
|
10L |
AA0065 |
|
Chelating Bestarose FF |
25mL |
AA206305 |
|
100mL |
AA206307 |
|
500mL |
AA0302 |
|
1L |
AA0303 |
|
5L |
AA0304 |
|
10L |
AA0305 |
Order information for IEX resins:
|
Resin |
Pack size |
Cat.No |
|
SP Bestarose FF |
25mL |
AI0011 |
|
100mL |
AI0012 |
|
500mL |
AI0013 |
|
1L |
AI0014 |
|
5L |
AI0015 |
|
10L |
AI0016 |
|
Diamond S |
25mL |
AI0181 |
|
100mL |
AI0182 |
|
500mL |
AI313311 |
|
1L |
AI0183 |
|
5L |
AI0184 |
|
10L |
AI0185 |
|
Diamond CD-S |
25mL |
AI05501 |
|
100mL |
AI05502 |
|
500mL |
AI05503 |
|
1L |
AI05504 |
|
5L |
AI05505 |
|
10L |
AI05506 |
Order information for mixed-mode resins:
|
Resin |
Pack size |
Cat.No |
|
Diamond MMC |
25mL |
AI0091 |
|
100mL |
AI0092 |
|
500mL |
AI305311 |
|
1L |
AI0093 |
|
5L |
AI0094 |
|
10L |
AI0095 |
|
Diamond MMC Mustang |
25mL |
AI0161 |
|
100mL |
AI0162 |
|
500mL |
AI305211 |
|
1L |
AI0163 |








.png)