Why IEX resin is used in processing of more than 70% bio-pharmaceuticals?
In the downstream processing of bio-pharmaceuticals, Ion exchange chromatography(IEX) enjoys advantages such as high resolution, large processing volume, easy operation and wide application, making it an indispensable part in the purification of macromolecules including antibody, vaccine and recombinant proteins.
Principle
IEX is a type of technology which achieves separation based on the electrostatic interaction of charges on the surface of molecules and resin beads. The target molecules are negatively or positively charged under certain pH condition, enabling its bind to cation or anion exchange chromatography resins. By adjusting pH and conductance in buffer system, efficient separation between target molecules and impurities can be achieved.
Protein titration curve
Protein titration curve is a key method for the understanding of IEX processing design by helping determine the suitable bind/elute condition.
• Each type of protein enjoys a unique net charge/pH relation, which can be presented by titration curve.
• Net charge on the surface of protein can change as pH varies. The right pH can make strength and property of net charge on the target protein surface different from those of other molecules, therefore achieving separation purpose by providing different binding strength between target molecules and resin compared with other molecules.
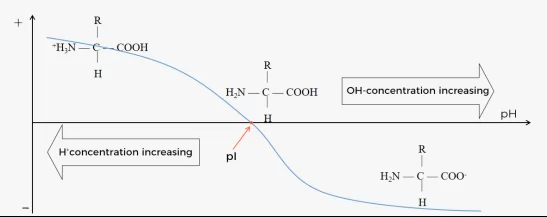
Note: when pH of solution is lower than the pI of molecule, molecule is positively charged(+) on the surface. when pH of solution is higher than the pI of molecule, molecule is negatively charged(-) on the surface.
Fig.1 Protein titration curve
Experiment process
• Equilibration: equilibrate with equilibration buffer until pH and conductance of column outlet buffer reach the same as equilibration buffer, which will usually take 3-5CVs.
• Load and wash: load sample according to binding capacity of the processing. Wash column with buffer till UV absorbance approaches baseline.
• Gradient elution: increase salt concentration in linear or step-wise format, elute substances from column according to different binding strength, collect fractions.
• Regeneration: Wash with high salinity solution (e.g. 1~2M NaCl, 0.1~0.5M NaOH). Wash with buffer till it is neutral.
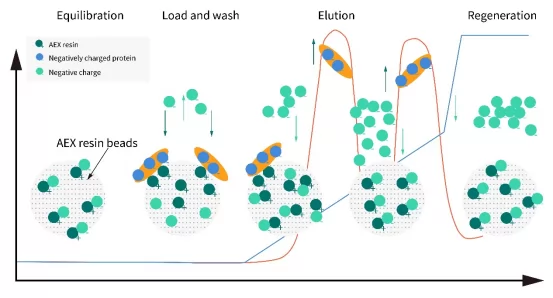
Fig.2 The flowchart of IEX chromatography
Key points of process optimization
• Choose the right resin and bead size
• Optimized buffer pH and buffer ionic strength
• Optimized parameters including elution methods and conditions for better separation.
As quality requirements for bio-products consistently improves, R&D of IEX resin and processing switches from ”standardized processing” to “refined control”.
The composition and classification of IEX resins
Composition
IEX resins consist of matrix and ligands.
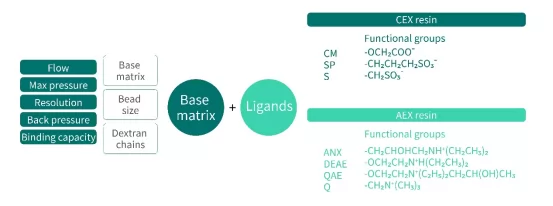
Fig.3 The composition of IEX resin
Classification
Based on the ligands, IEX resins fall into two categories:
• Cation Exchange Resins:Negatively charged ligands, bind to positively charged molecules. E.g. Sulfonic acid (SP), carboxyl group(CM)
• Anion Exchange Resins: Positively charged ligands, bind to negatively charged molecules. E.g. Quaternary amine (Q), diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)
In addition, adaption of ligands at different pH condition shall be determined based on dissociation degree of ligands at different pH condition as well as ionic strength of ligands.
Table 1. Characteristics of IEX resins
|
Type |
Ligands |
pKa/ property |
pH range |
Features and applications |
|
Strong CEX resins |
Sulfo groups(e.g. SP,S) |
Not being impacted by pH, remains positively charged. |
2–12 |
High dissociation degree, suitable for dramatic pH variation. Suitable for protein with low pI(e.g. lysozyme, trypsin inhibitor) |
|
Weaker CEX resins |
Carboxy groups(e.g. CM) |
pKa ≈ 4–5 |
4–9 |
Sensitive to pH, higher resolution, separation is performed with mild condition. For example, acidic protein or molecules which are sensitive to strong acid. |
|
Strong AEX resins |
Quaternary ammonium group(e.g. Q) |
Remains positively charged(not being impacted by pH) |
2–12 |
Strong binding, suitable for the processing of alkaline stable proteins with high pI(e.g. serum albumin, IgG) |
|
Weak AEX resins |
Diethylaminoethyl(DEAE) |
pKa ≈ 9–10 |
6–9 |
Suitable for neutral to alkaline condition, mild elution, suitable for the processing of alkaline-instable proteins(e.g. vaccine antigen or DNA/RNA molecules) |
Tips for application
• Choose strong IEX resins when wider pH stability and higher binding strength are required.
• Choose weak IEX resins when better selection and milder B/E conditions are required.
• Strong IEX resins are intended for standard processing operation on scale-up, while weak IEX resins are intended for purification of specific proteins.
IEX resins from Bestchrom
Bestchrom offers a wide range of IEX resins for different applications.
Table 2. Bestchrom IEX resins
|
Resin type |
Features |
Resin name |
Applications |
|
Agarose based IEX resin |
Fast flow |
Q/DEAE/SP/CM Bestarose FF |
The most widely applicable |
|
High resolution |
Q/DEAE/SP Bestarose HP |
When high resolution is required |
|
High binding capacity |
Q/SP Bestarose XL |
Viral purification |
|
Big beads |
Q/SP Bestarose BB |
Highly viscous feedstock |
|
Big beads & high binding capacity |
Q/SP Bestarose XL BB |
Low content, large volume, high viscosity |
|
High rigid agarose based IEX resin |
High max pressure |
Diamond Q/DEAE/S/CM |
Replace agarose matrix |
|
High resolution |
Diamond Q/DEAE/SP Mustang |
High resolution, antibody purification |
|
High binding capacity & high resolution |
Diamond CD-S |
Antibody purification |
|
Polymer based IEX resin |
High resolution |
BestPoly 15/30S/Q |
Purification of adenovirus, insulin and peptide |
|
High binding capacity & high resolution |
MegaPoly BXS |
Polishing of antibody |
|
Dextran based IEX resin |
|
CM Bestdex C-25 |
antibotics |
|
|
DEAE Bestdex A-50 |
Prothrombin complex |
Application
IEX is widely used in the following applications:
• Intermediate and polishing of antibody, for the removal of impurities.
• The removal of virus-related impurities in vaccine production
• The efficient capture of recombinant proteins.
Case Study
Diamond CD-S resin used for the purification of mAb
• Sample:mAb,pH5.0,conductance 4mS/cm
• Buffer A:50mM NaAc-HAc,pH5.0,Cond:4mS/cm
• Buffer B:50mM NaAc-HAc + 0.5M NaCl,pH5.0
• Buffer C:0.5M NaOH
• Column:Diamond CD-S
• Column size:BHR 5/17,2mL,bed height 10cm
• Flow:6RT
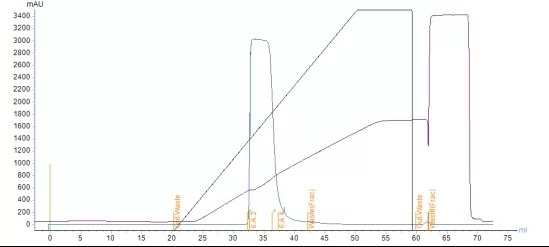
Fig.4 Diamond CD-S chromatogram
Results
Table 3.Results
|
Resin |
Sample |
Volume
(mL/CV) |
Conc.
(%) |
Yield (%) |
SEC |
CE-non-reduction |
CEX |
HCP
(ppm) |
Aggregate
(%) |
Monomer
(%) |
IgG monomer protein(%) |
Acid peak(%) |
Main peak(%) |
Basic peak(%) |
|
|
|
Original sample |
11.60 |
6.84 |
|
0.87 |
99.13 |
97.53 |
23.83 |
58.98 |
17.18 |
90.11 |
|
Diamond CD-S |
2000-2000E |
3.66 |
18.18 |
83.87 |
0.15 |
99.85 |
97.86 |
22.80 |
61.21 |
15.99 |
3.17 |
Conclusion
In the downstream bioprocessing, IEX resins are both useful tools for separation, as well as efficient solutions to quality products with high purity. A good understanding and mastery of it is a compulsory course for bioprocessing developers.
Bestchrom provides Diamond CD-S and MegaPoly BXS resins for the efficient, accurate and stable purification of mAb, BsAb and ADC, contributing to the process optimization and cost reduction of biopharmaceuticals.
Order Information
|
Resin |
Pack size |
Cat.No. |
|
Diamond CD-S |
25mL |
AI05501 |
|
MegaPoly BXS |
25mL |
AT05701 |







.png)