A Brief Introduction of Plasmid Purification
As early as 1840s, scientists discovered cytoplasmic genetic factors which can metastasize among cells. In addition, scientists proposed many assumptions including parasites, symbiotes and genes. However, a particular name was not defined.
It was not until 1952, Joshua Lederberg started to categorize these cytoplasmic genetic factors and came up with the term “Plasmid” for the first time. “Plasmid” is a combination of “Cytoplasm” and “id” (which means “it” in Latin), which later became a common term for any extra-chromosomal genetic determinants.
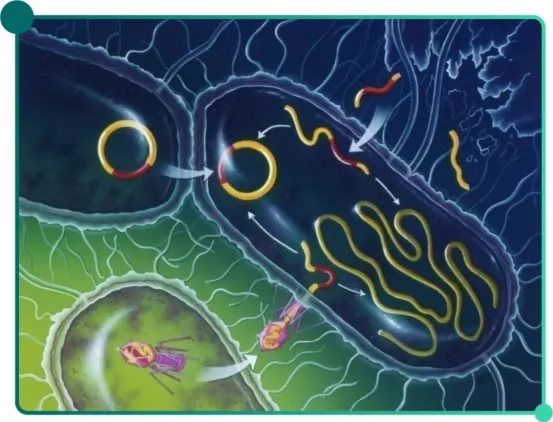
Fig.1 Plasmid
Plasmid is loop superhelix double strand DNA, which is able to replicate and inherit in host cells independent of chromosome. Besides, plasmid can act as gene vector once being coupled with foreign DNA via genetic engineering, before entering into host cells.
Today, plasmid is acting as one of the most important tools in biopharmaceutical industry, which is widely used in the cloning, expanding and expression of target proteins. In addition, plasmid also plays an important role in viral vector and mRNA production.
Plasmids have a variety of topology structure, including supercoiled plasmids, open circular plasmids, and linear plasmids. Among which supercoiled plasmid is most active while open circular plasmid content needs to be strictly limited in the finished products due to its poor performance in cell transduction.
Bestchrom R&D team has developed a three-step approach for plasmid purification, which enjoys great stability, high efficiency and easy scale-up. Therefore, the approach saves customer efforts in the obtaining of highly purified plasmids to meeting high standard.
Plasmid Production
-
Bacteria fermentation
-
Harvest of Bacteria
-
Bacterial lysis
-
Clarification and filtration
-
Ultrafiltration and buffer exchange
-
Size exclusion chromatography
-
Affinity chromatography
-
Anion exchange chromatography
-
Concentration and buffer exchange
-
Sterilization and filtration
Purpose of Plasmid Production
-
The obtaining of certain level of highly purified supercoiled DNA (scDNA)
-
Removal of product related impurities: open circular DNA(ocDNA), plasmid DNA aggregates (dimer, trimer, tetramer, etc.)
-
Removal of process related impurities: HCP, HC-DNA, HC-RNA
-
Control biological load: endotoxin and microorganism
-
Robust process chain, easy repeatability
-
Easy scale-up
Plasmid Purification Technology
Bestarose 6FF chromatography
-
Sample preparation: Concentrated sample with hollow fiber
-
Bestarose 6FF chromatography is intended for the rapid removal of RNA, with yield higher than 90%
-
Buffer: 2.1M(NH₄)₂SO₄-10mM EDTA-100mM Tris, pH7.5
-
Optional column bed height: 30-50cm
-
Sample loading volume: 15-25% CV
-
Operating flow rate: 60-120 cm/h
-
Supercoiled plasmid accounts for 80% and above in the collected flow-through.
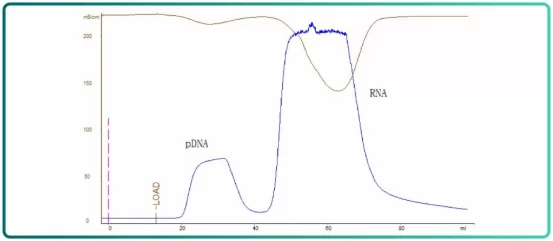
Fig.3 SEC(Bestarose 6FF) chromatogram
Plasmid affinity chromatography
Efficient removal of supercoiled plasmid (sc DNA) and open circular plasmid (ocDNA). In the removal of ocDNA, yield can generally reach higher than 80%, yield of scDNA can be as high as 95% after the purification step.
Buffer A: 2.1M(NH₄)₂SO₄-10mM EDTA 100mM Tris, pH7.5
Buffer B: 1.7M(NH₄)₂SO₄-0.3M NaCl-10mM EDTA-100mM Tris, pH7.5
-
Alkali washing: 0.5M NaOH 2~3CV, leave it undisturbed for 15~30min
-
Washing: 2-3CV of distilled water
-
Equilibration: Wash with buffer A 2-3CV, till PH and conductivity are balanced
-
Load sample: No more than 2.5mg/mL, retention time no lower than 3min
-
Washing: Wash with 3-5CV of Buffer A
-
Elution: Elute with Buffer B
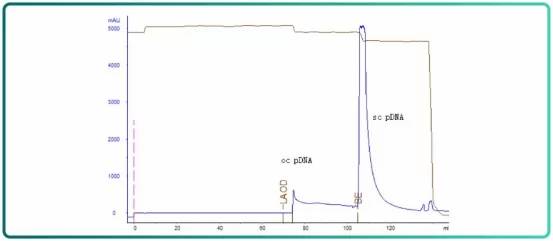
Fig.4 Affinity chromatogram
Q Mustang Anion Exchange Chromatography Resin
Remove the endotoxin residual and trace impurities by using the high resolution of the resin, with normal yield higher than 80%
Buffer A:0.4M NaCl-10mM EDTA-100mM Tris, pH7.5
Buffer B:1.0M NaCl-10mM EDTA-100mM Tris, pH7.5
Sample: Dilute affinity eluent and TE Buffer according to ratio of 1:2
Chromatography procedure:
-
Alkali washing: 2~3CV of 0.5M NaOH, leave it disturbed for 15~30min
-
Washing: 2-3CV of distilled water
-
Equilibration: Wash with 2-3CV of buffer A, till PH and conductivity are balanced.
-
Load sample: No more than 2mg/mL, retention time no lower than 3min
-
Washing: Wash with 3-5CV of Buffer A
-
Elution: Elute with Buffer B
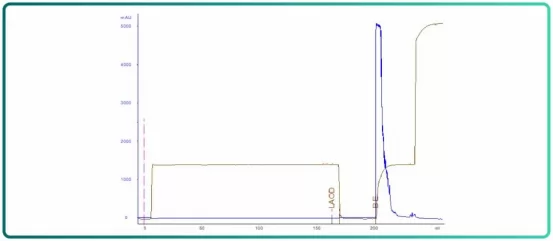
Fig.5 SEC chromatogram
Experiment Results Analysis
For convenient experiment data analysis after performing plasmid purification with our resin, Ezscreen Bestarose 6HP is a pre-packed column launched by Bestchrom for the quantitative analysis of plasmid.
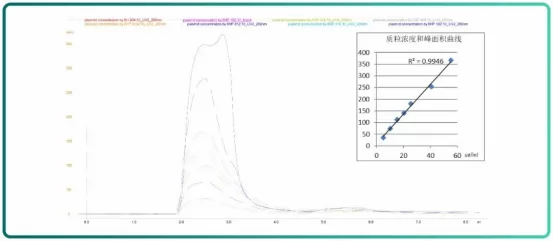
Fig.6 Plasmid analysis chromatogram
Resins used in three-step plasmid purification
|
Resin
|
Resin type
|
Purification purpose
|
Average particle size
|
|
Bestarose 6FF
|
Gel filtration
|
Removal of RNA
|
90μm
|
|
Plasmid Cap Mustang/HP
|
Affinity chromatography
|
Removal of open circular plasmid
|
40/34μm
|
|
Diamond Q Mustang / Q Bestarose HP
|
Anion exchange chromatography
|
Removal of endotoxin
|
40/34μm
|







.png)